Japan Introduces Humanoid Robot for Railway Line Maintenance
Find out how Japan’s new 12m tall humanoid robot is providing versatility for maintaining the railway.
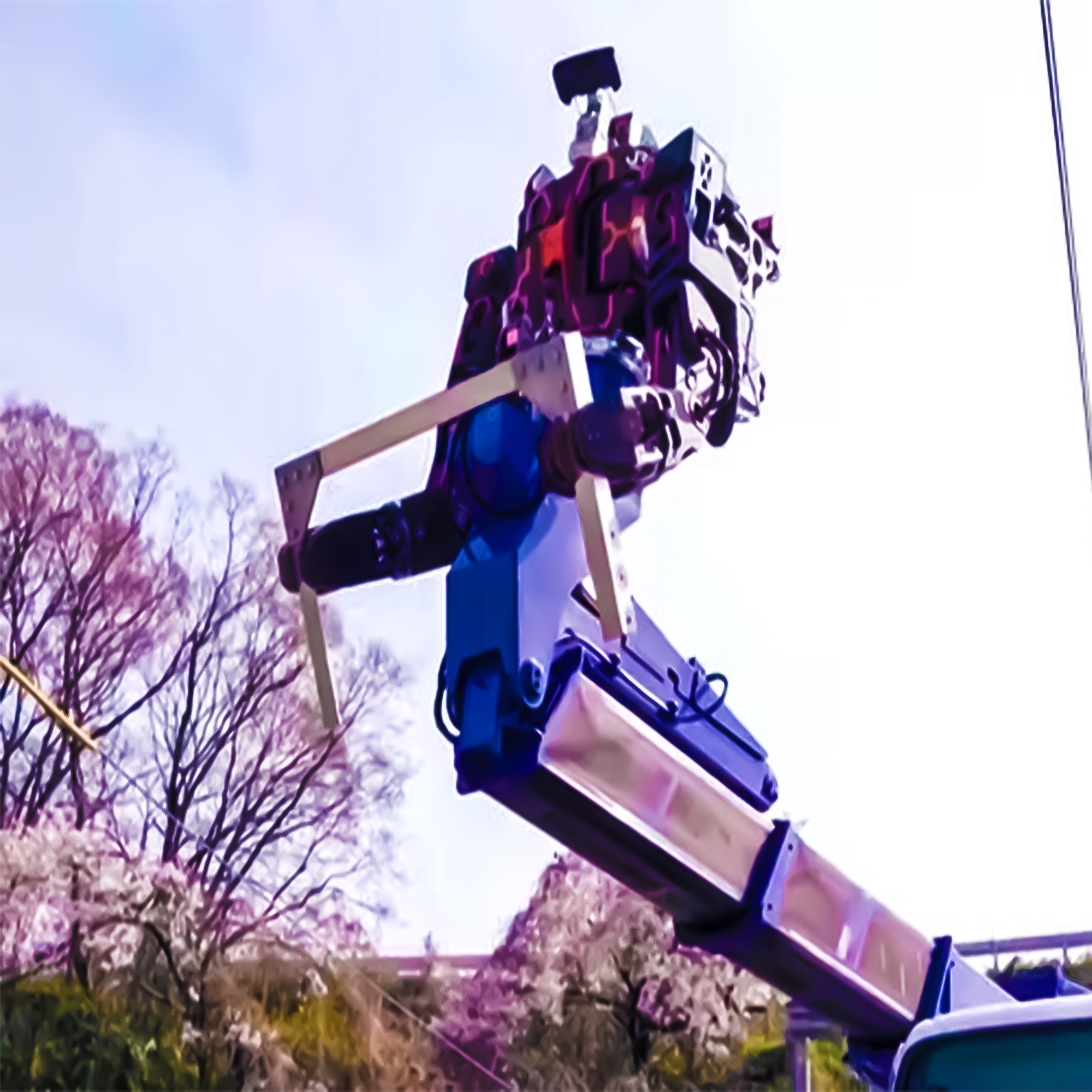
Japan takes a jump into the future with the creation of a humanoid robot: it is supposedly wired to monitor railway tracks. What is said to replace the E6 Shinkansen bullet trains, the Bot, of extraordinary design, is a 12-meter high thing of sheer splendor. Most synonymous with the coke bottle eyes and a head similar to Wall-E, the Bot also has arms powerful enough to hold blades or a paintbrush. Find out more about Japan’s newest entry in the blog.
The Role of the Humanoid Robot
1. Versatile Maintenance Capabilities
The humanoid robot has been designed to perform diverse work on the maintenance of railway lines. It can change arms with newly developed devices, among them a blade for precision cutting, or a paintbrush for spreading coatings, flexing to its adaptability to different maintenance tasks.
2. Improved Efficiency and Safety
Japan is deploying the use of the humanoid robot with the target of capacitating its railway operation service. The robot can undertake its work with a very high degree of precision; therefore, Japan has minimal chances of error, hence leading to an upgrading of safety standards, which would be important in this compliance-needed railway environment.
This makes it a telling example of Japan’s innovations in engineering, and the unique design characteristics, such as its eyes and head, make the robot stand tall even while enabling it to function in a wide variety of hazardous conditions.
3. Adoption of AI in Advanced Robotics
A humanoid robot is a symbiosis of advanced robotics and artificial intelligence through which it can independently be guided to move in complex ways and show many actions. This becomes a telling example of Japan’s effort to introduce artificial intelligence in maintaining infrastructures.

Impact on Railway Industry
1. Future Prospects
As Japan becomes the pioneer in introducing humanoid robots for railway maintenance, the technology presents a new way of doing business around the world in that industry. This is because the incorporation of the humanoid robots in the rail infrastructure could lead to the reduction in maintenance costs and improved operational efficiency.
3. Comments and Public Reaction
An overview of people’s reactions shows that stakeholders wait with a sense of both curiosity and optimism the spread of these robots across the extensive railway network of Japan.
Conclusion
In this sense, Japan has stepped to another level upon introduction of the humanoid robot into the railway maintenance. The robot represents not only a level of innovation and multifunctional capacity on the part of Japan’s technological capabilities, and it very well may be the model of the future with respect to railway maintenance and more.
Remain updated with the recent new advances in the field of robotics and infrastructure maintenance!
— Dr. Hiroshi Yamamoto, Robotics Engineer

Our humanoid robot represents a leap forward in
railway maintenance technology, combining AI and
robotics for enhanced efficiency.